
Welcome to a page of images contributed by BHAS member Richard Walker.
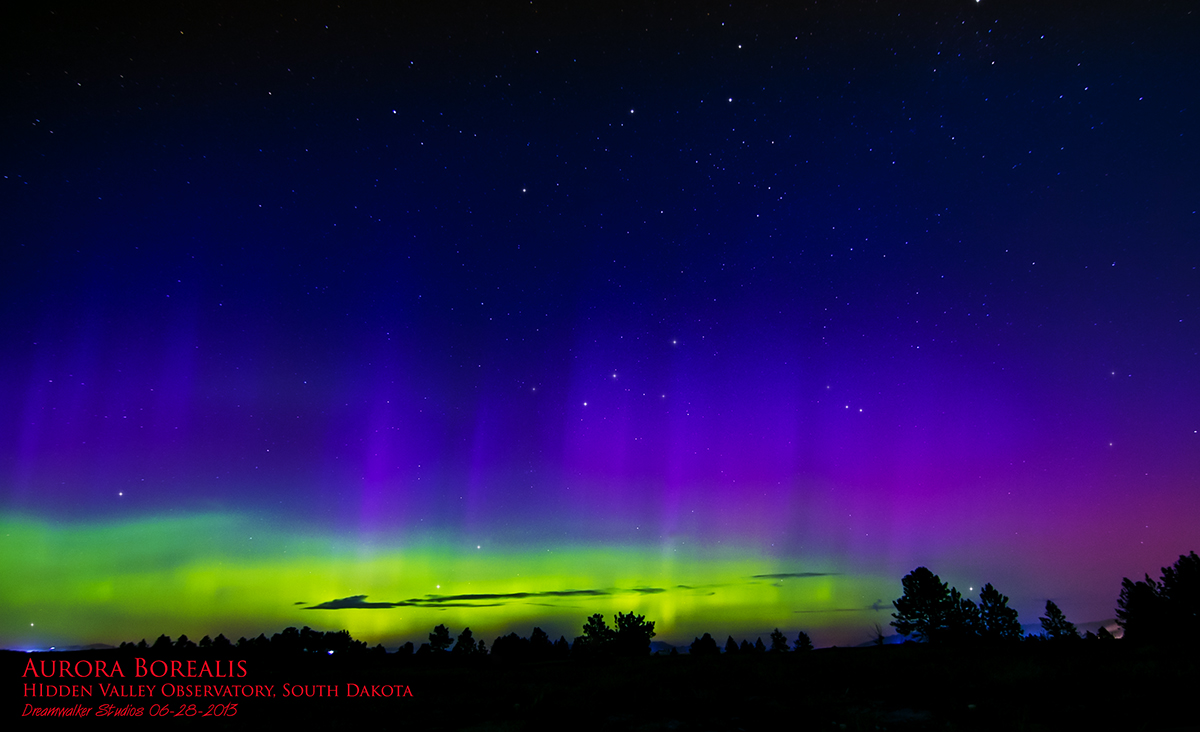
An image of the Aurora Borealis
captured at the Hidden Valley Observatory on June 28, 2013 at 23:47 MDT by
Richard Walker using a tripod-mounted Canon 60-D DSLR with a Tokina 11-16mm
f/2.8 lens set at
11mm focal length and an aperture of f/2.8. The white balance was set at
"daylight", the sensitivity at
ISO 800 S-RAW, and the shutter speed at 10 seconds.

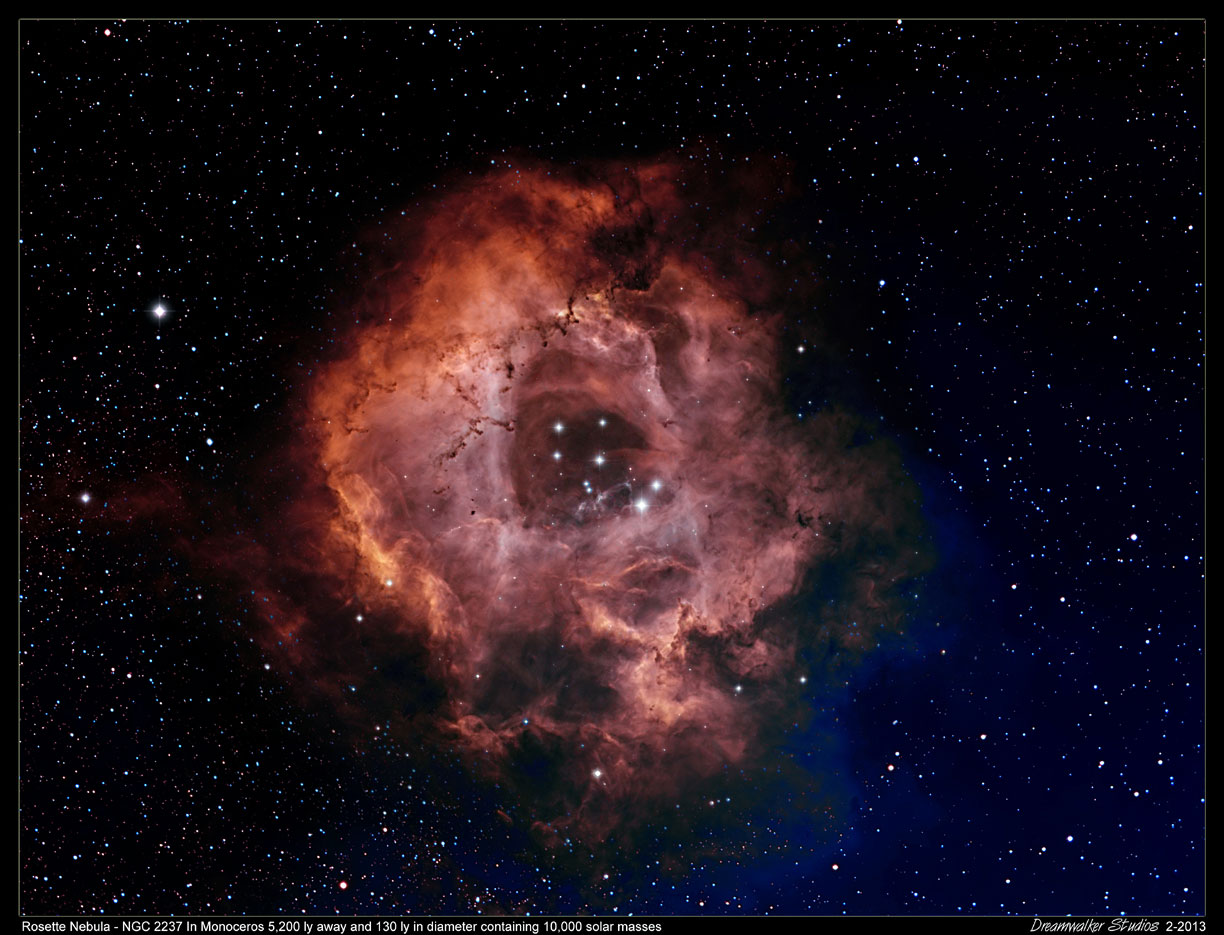
The Rosette Nebula, NGC 2237 in
Monceros, is 5200 light-years distant and 120 l.y. in diameter
containing 10,000 solar masses. Imaged February, 2013.

******
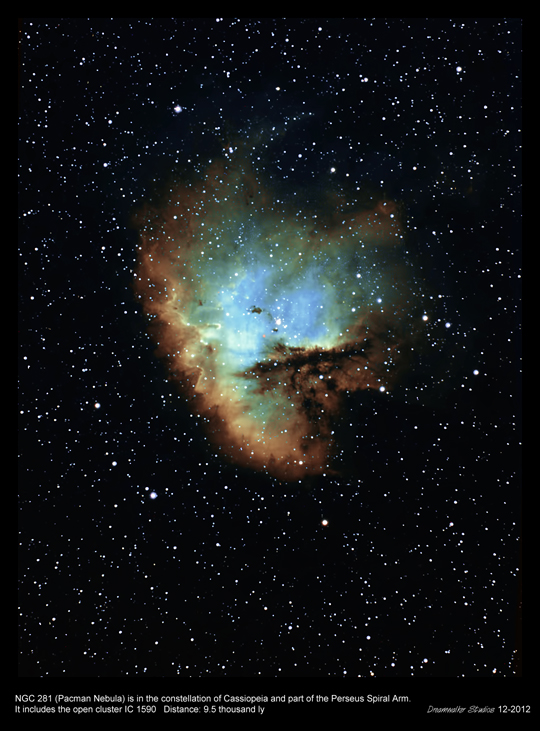
The
Pacman Nebula. (NGC 281 in Cassiopeia) Total integration 7.5hrs
(Technical details below image)

Imaging Camera: ATIK
314L+ Mono
Mount: Losmandy
G11 Gemini 2
Polar
Alignment Software: Align Master and Gemini 2
Target
Acquisition Software: SkyTools
Imaging
Scope: TMB 92 mm, Triplet (Reduced to 405mm with TeleVue TRF-2008
Reducer/Flattener)
Image
Acquisition Software: Nebulosity v3
Guide
Scope: Vixen 70mm f/12.9 (fl: 900mm)
Guide
Camera: Starlight Xpress Lodestar Autoguider
Guide Software: Stark Labs PHD
Image
Scale: 3.28 arcsec/pix
Field of
view: 56.9 x 76.2 arcmin
Image
Integration Time: SII 15 x 10 min., Ha 10 x 10 min., OIII 20 x 10 min.
Image
Acquisition Date: Dec. 12, 16, 19 - 2012
Image
Calibration Software: Nebulosity v3
Image
Color Mapping and Processing: Photoshop 7.0
Color
Assignment:
Hubble Palette (SHO): Image was created by mapping the SII, Ha and OIII data
respectively to the R, G and B channels.
Narrowband
Filters: Astrodon SII 5nm, Ha 5nm, OIII 3nm
******
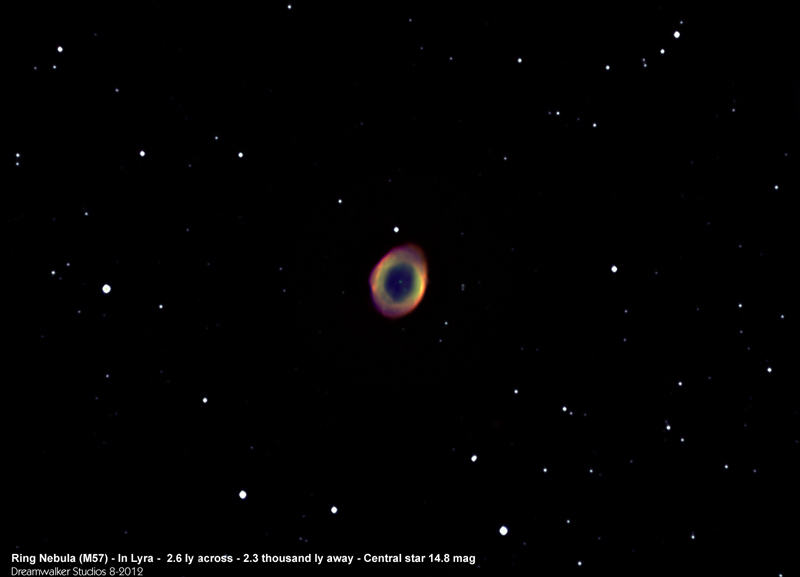
The famous Ring Nebula (also catalogued as Messier 57) appears in the northern constellation of Lyra. It is a prominent example of a planetary nebula. But when it was discovered by the French astronomer Antoine Darquier de Pellepoix in January 1779, and a month later by French astronomer Charles Messier while he was searching for comets, it was speculated that the nebula was formed by multiple faint stars that could not be resolved with their telescopes.
Today we now know this is is a shell of ionized gas expelled into the surrounding interstellar medium by a red giant star, which was passing through the last stage in its evolution before becoming a white dwarf. (Information Source: Wikipedia)

*******
NGC 4565, also
known as the Needle Galaxy, is an edge-on spiral galaxy
30 million light-years distant and
spans over 100,000 light-years in diameter
in the constellation Coma
Berenices.
The 10th magnitude
galaxy sits perpendicular to our own Milky Way Galaxy and is almost directly
above the North Galactic Pole, in the same way Polaris is located above the
Earth's North Pole.
First spotted in
1785 by Sir William Herschel, this is one of the most famous examples of an
edge-on spiral galaxy. NGC 4565 is considered by some to be a prominent
celestial masterpiece Messier missed.
To the lower right is its companion galaxy NGC 4562.

******
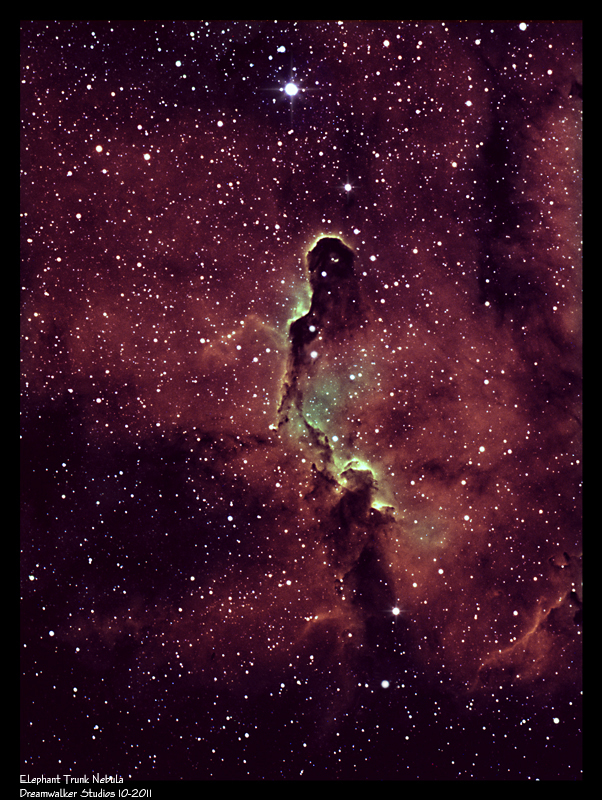
The Elephant Trunk Nebula winds through the emission nebula and young star cluster complex IC 1396, in the high and far off constellation of Cepheus. This beautiful area of hydrogen gas and dust is a stellar nursery that holds many young nascent stars. The top region of the Elephant Trunk is being blown away by radiation emitted from new-born stars that are igniting deep within the nebula.
This cosmic elephant's trunk is over 20 light-years long and about 2,400 light-years away from Earth.
The
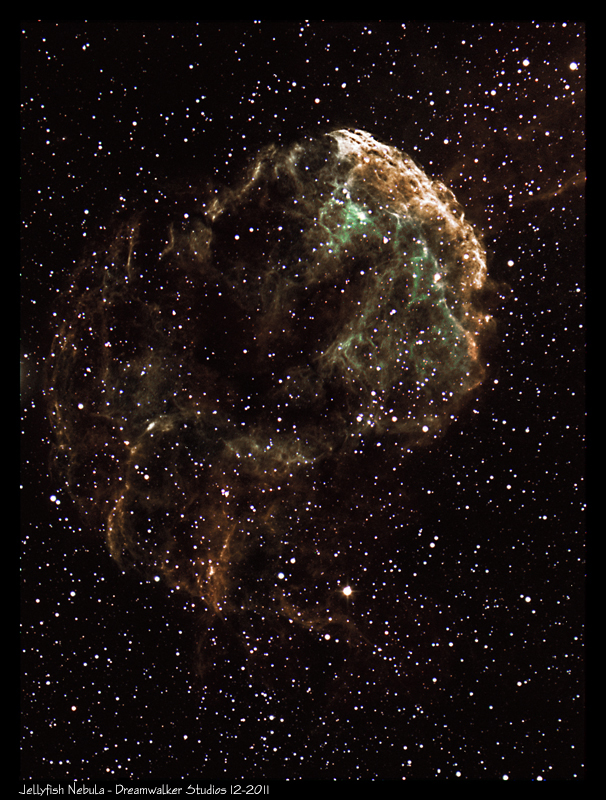
Jellyfish Nebula, also known as IC 443, is a Galactic supernova
remnant in the constellation Gemini with an estimated distance of 5,000 light
years from Earth.
The remnant's age
is still uncertain. But there is some agreement that the progenitor supernova
happened between 3,000 and 30,000 years ago.
The same supernova event likely created a neutron star, the collapsed remnant of the stellar core. IC 443 is one of the best-studied cases of supernova remnants interacting with surrounding molecular clouds.
The
Leo Triplet, also known as the M66 Group, is
a gathering of three magnificent
galaxies in one field of view
about 35 million
light-years away in the constellation Leo. This galaxy group consists of the
spiral galaxies M65, the M66, and the NGC 3628.
NGC 3628 is seen edge-on,
with obscuring dust lanes cutting across the plane of the galaxy, while the
disks of M66 and M65 are both inclined enough to show off their spiral
structure. Gravitational interactions between galaxies in the group have also
left telltale signs, including the warped and inflated disk of NGC 3628 and the
drawn out spiral arms of M66. This gorgeous deep view of the region spans about
one degree (two full moons) on the sky. The field covers over 500 thousand
light-years at the trio's estimated distance of 30 million light-years.
IC 2745, upper left of the
image, is a spiral 14.5 magnitude galaxy with a red shift of 0.03380.
